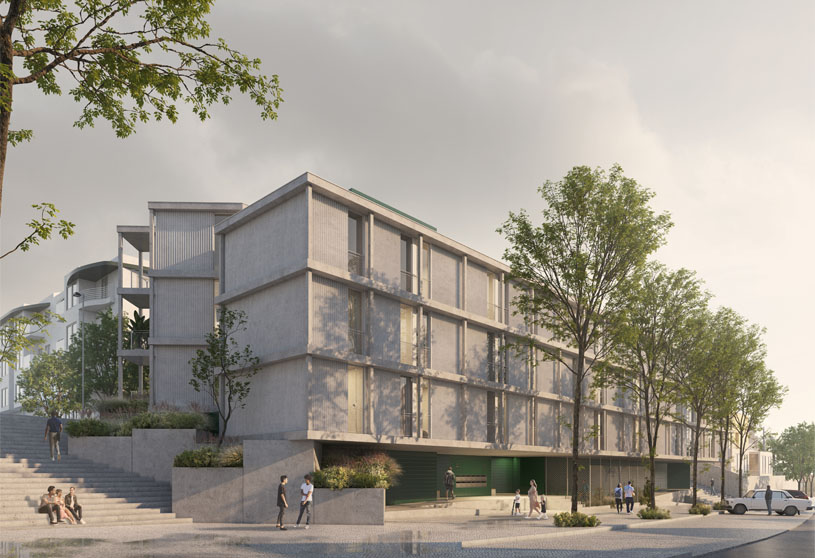
Excerpt: Plot C – ICARO, designed by MASSLAB, is a housing project that mimics the topographic mismatch of the site by dividing the block into two distinct volumetric bodies, which assume different characters, related to the urban contexts of the two levels. The design seeks to find the unobstructed visual threads and a better solar orientation. The volume itself takes on two dimensions volumetrically. The proposed landscape integration enhances everyday living and provides a greater relationship with outdoor spaces.
Project Description
[Text as submitted by architect]
ICARO
“Icaro” appears out of the requirement to create continuity between existing spaces and future realities. Integration into the urban fabric alone is not enough, people are fundamental in the process. Thus emerges Icaro, which subtly turns toward the sun.
CONTEXT
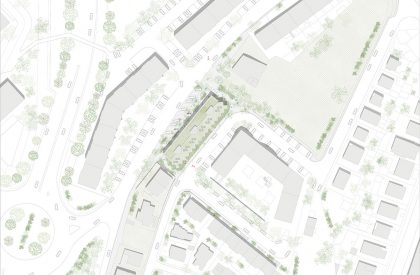
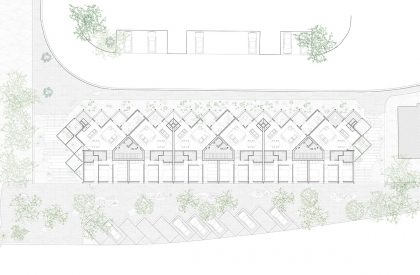
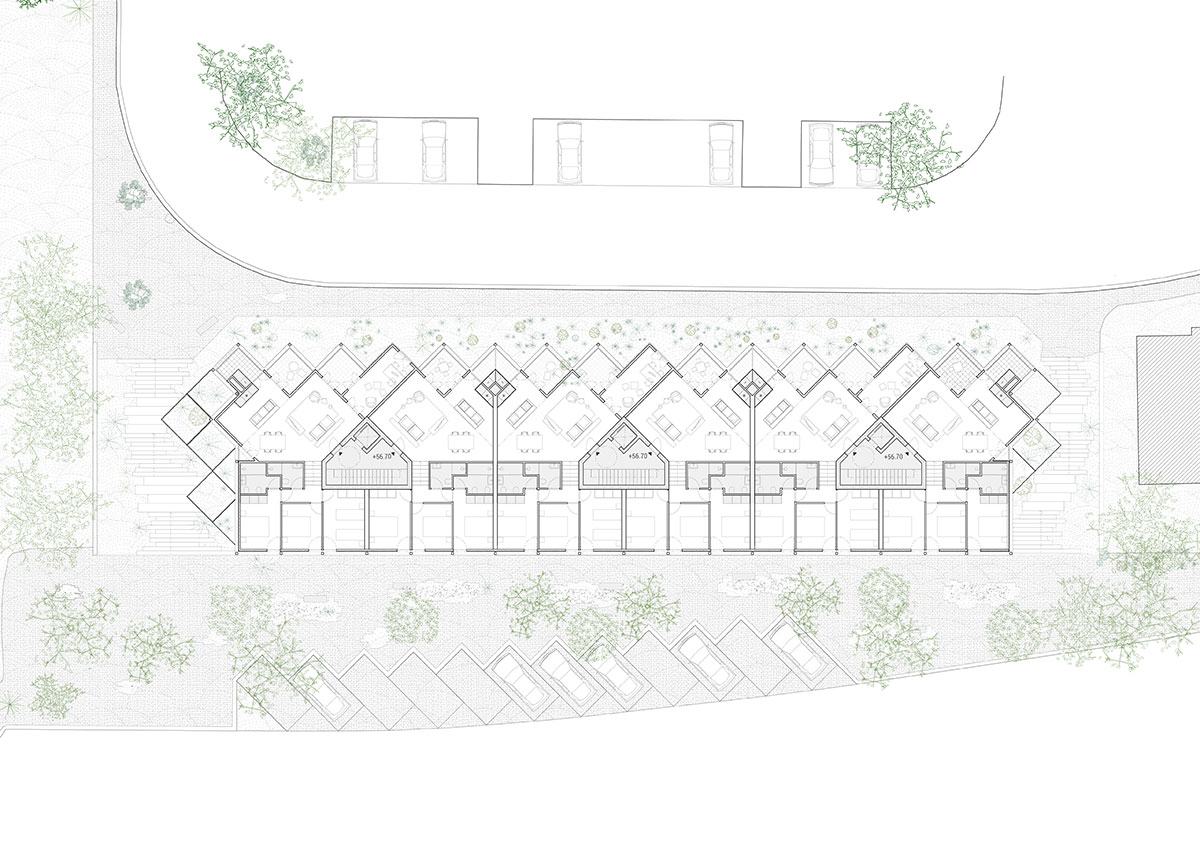
The intervention area is located in Quinta do Pombal, in Monte da Caparica, establishing a relationship at low elevation with Rua Lino Lima and at high elevation with Rua dos Carlos Reis. The immediate surroundings are mainly composed by housing and a university and research campus at high elevation. In order to mitigate/dilute the discrepancy between the peripheries and the city center, the proposal should ensure the creation of alternative programs and spaces that encompass local communities without segregating them from each other.

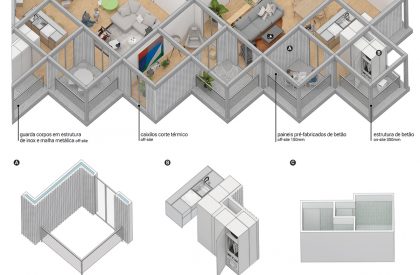
INTEGRATION AND CONSTRAINTS
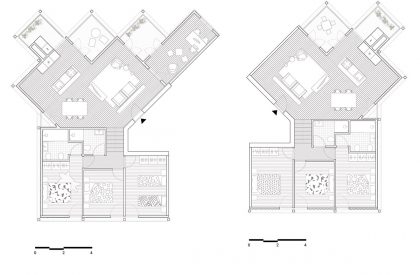
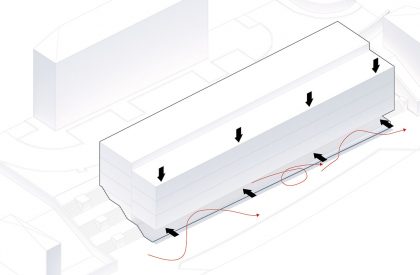
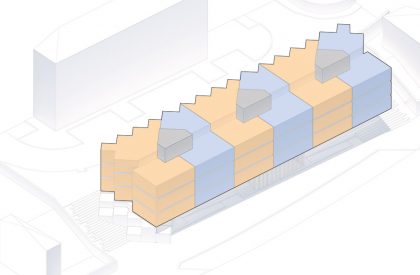
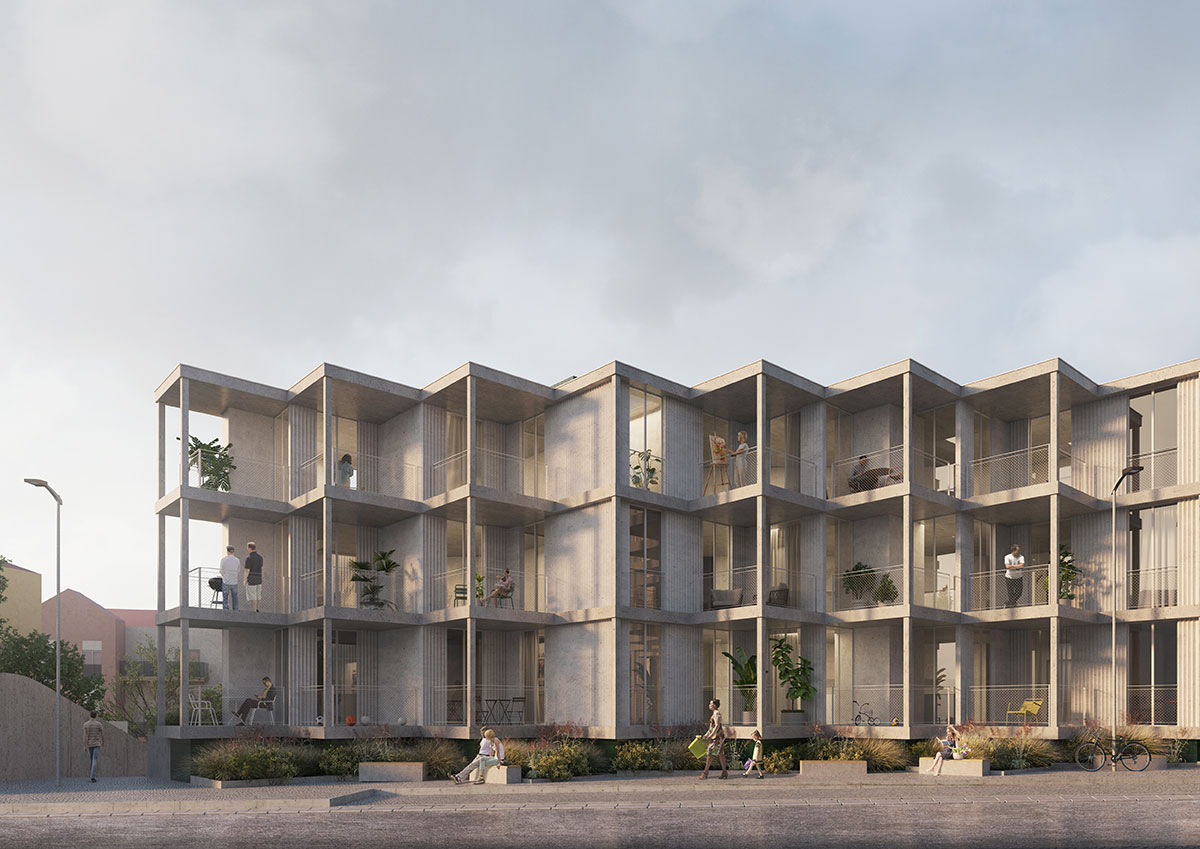
When we look at the surroundings, we realize that this area is residential, and that there is an apparent lack of permanent spaces and buildings that create the backdrop for this social interrelationship to occur. The only public spaces present are associated with academic work, and lack the character necessary to create urban social context. The proposal mimics the topographic mismatch of the site by dividing the block into two distinct volumetric bodies, which assume different characters, related to the urban contexts of the two levels.
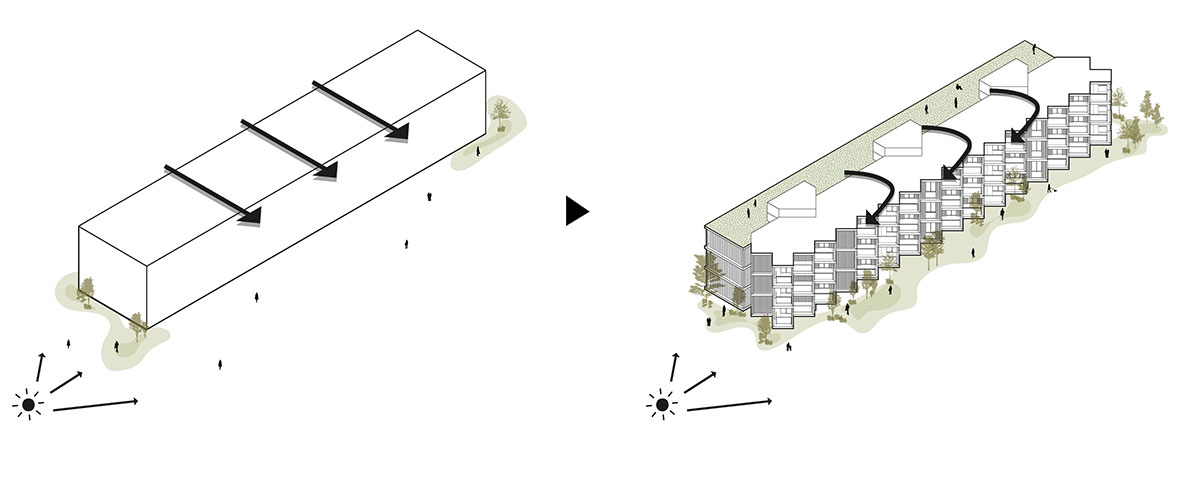
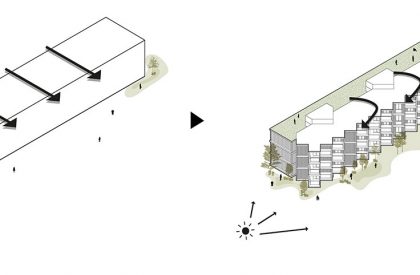
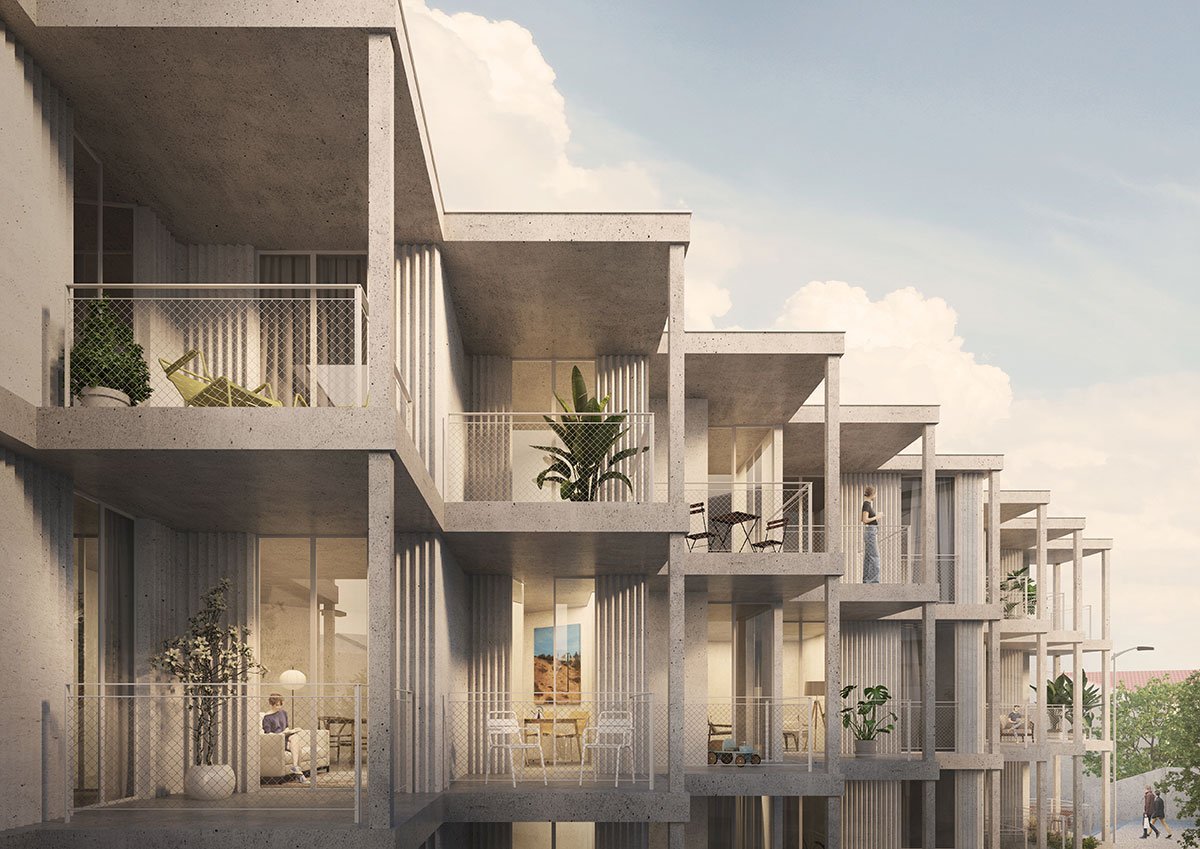
SOLAR ROTATION/ARTICULATION OF THE BUILDING
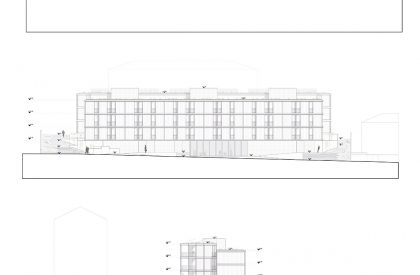
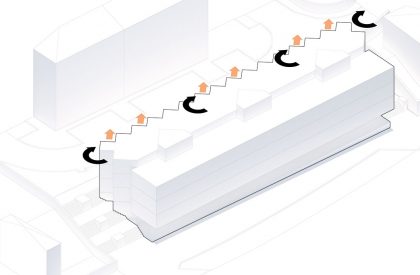
Like the Greek mythological character, the proposed Icarus seeks to get closer to the sun. The immediate surroundings are marked by continuous and monotonous buildings. Facing this density and evidencing the programmatic division of the interiors in the behavior of the façade. The design seeks to find the unobstructed visual threads and a better solar orientation. The torsion also gives way to a system of balconies that mediate the relationship between interior and exterior, between public and private, promoting a sense of neighborhood. The volume itself takes on two dimensions volumetrically.

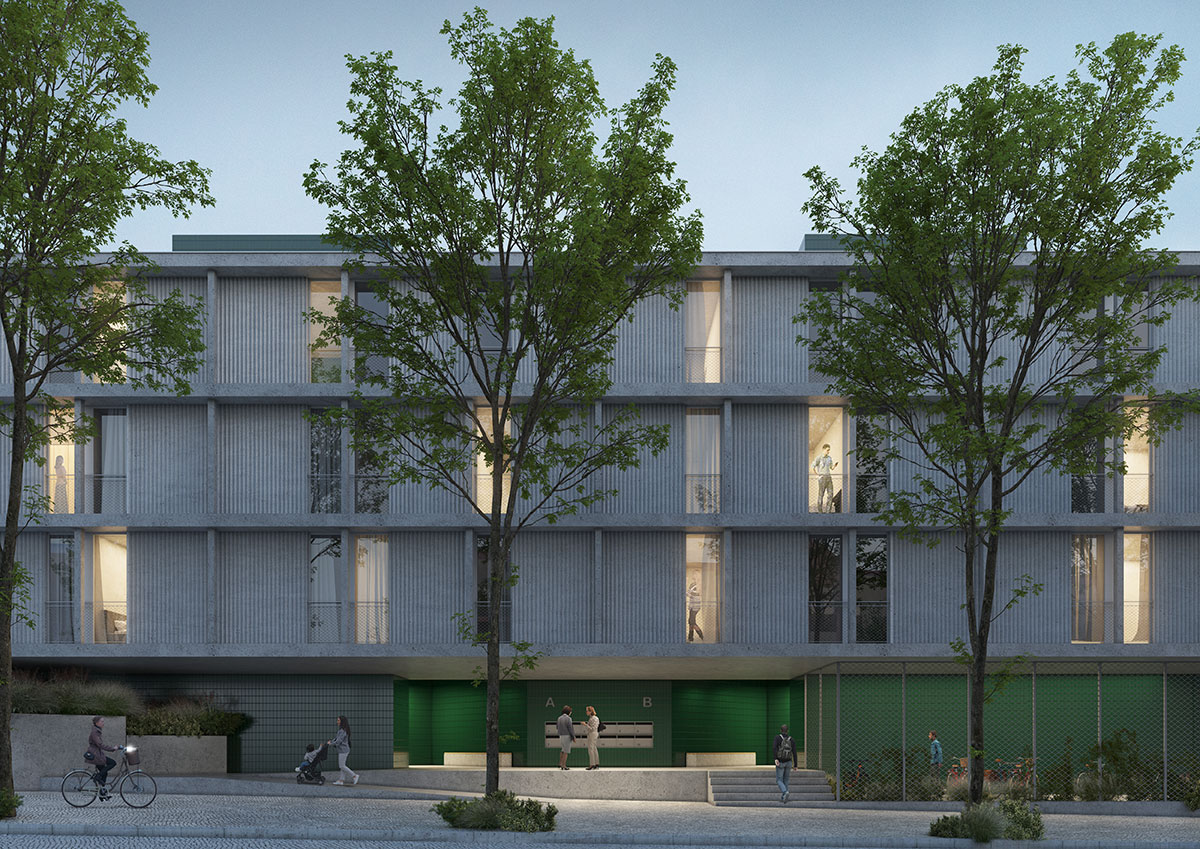
FLUID RIGIDITY
Different lifestyles result in typologies with varying degrees of flexibility. The building’s façade intends to reflect this duality through the use of two types of prefabricated paneling with contrasting roughness. This solution allows for faster construction and more efficient, less interventionist, and less expensive maintenance. The clarity of the constructive action, intends to evidence a technical rationality materialized in a rational main structure colmated by a set of prefabricated and modular elements, whose manufacture is done in controlled environments and planned for a rapid application, promoting an efficient use of materials, labor and time spent.

THE SIMPLIFIED SYSTEM
The use of prefabricated panels, in addition to the economic benefits of production, also allows greater control over the quality of the final finish. These types of facades are also very resilient, allowing for the optimization of maintenance costs throughout the building’s useful life. The choice of texture is due to the fact that it hides the joints between panels, ensuring the continuity of the facade. In this way, it is possible to reconcile the benefits of prefabrication with the intended façade strategy.
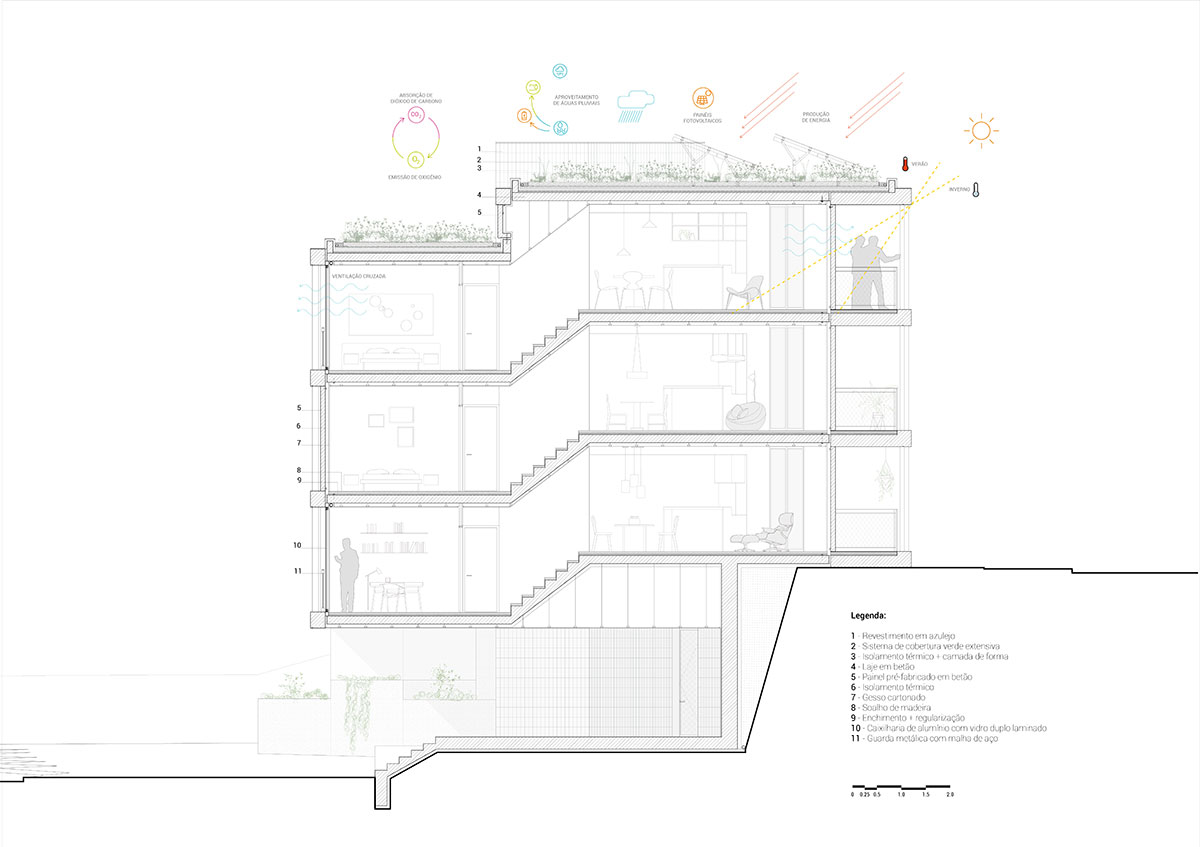
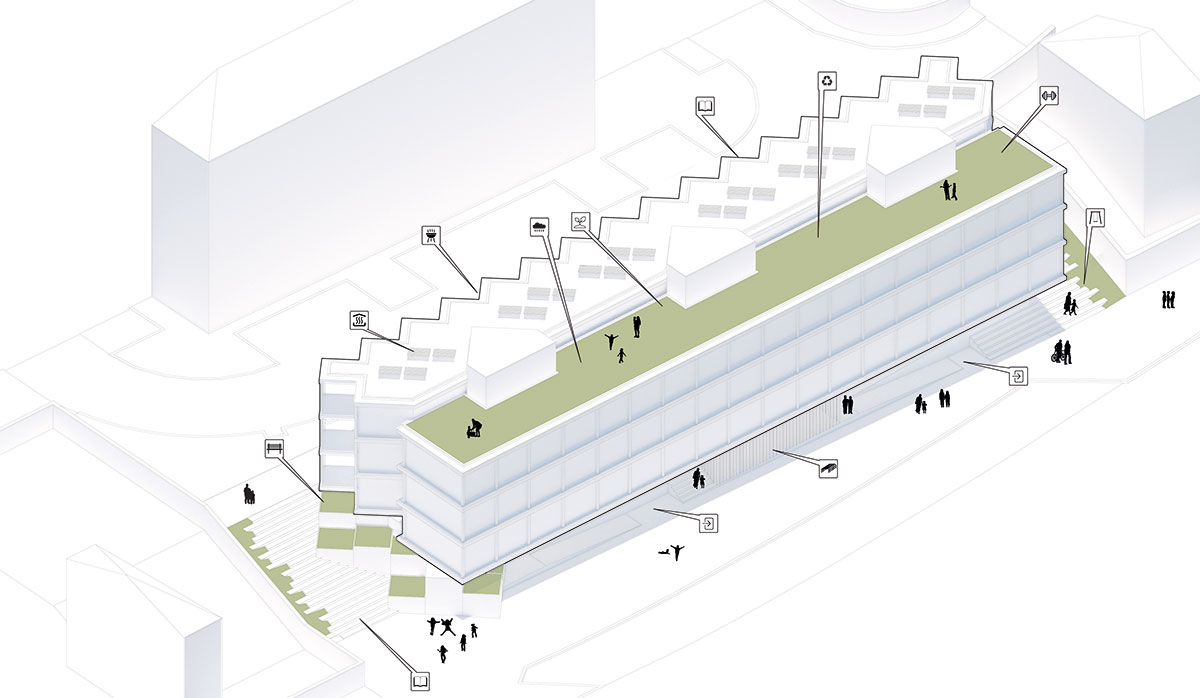
LANDSCAPE DESIGN
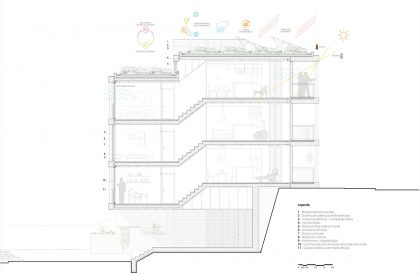
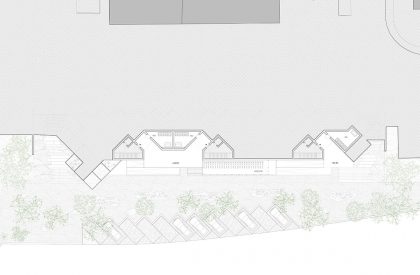
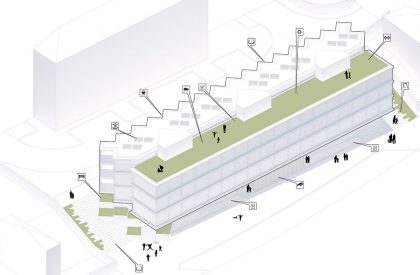
The proposed landscape integration enhances everyday living and provides a greater relationship with outdoor spaces through accessibility, social cohesion, safety, and the scenic value. The proposal proposes special attention to the integration of the staircases with a natural relation with vegetation, in order to soften the built character of the landscape, increasing the general permeability of the exterior spaces.
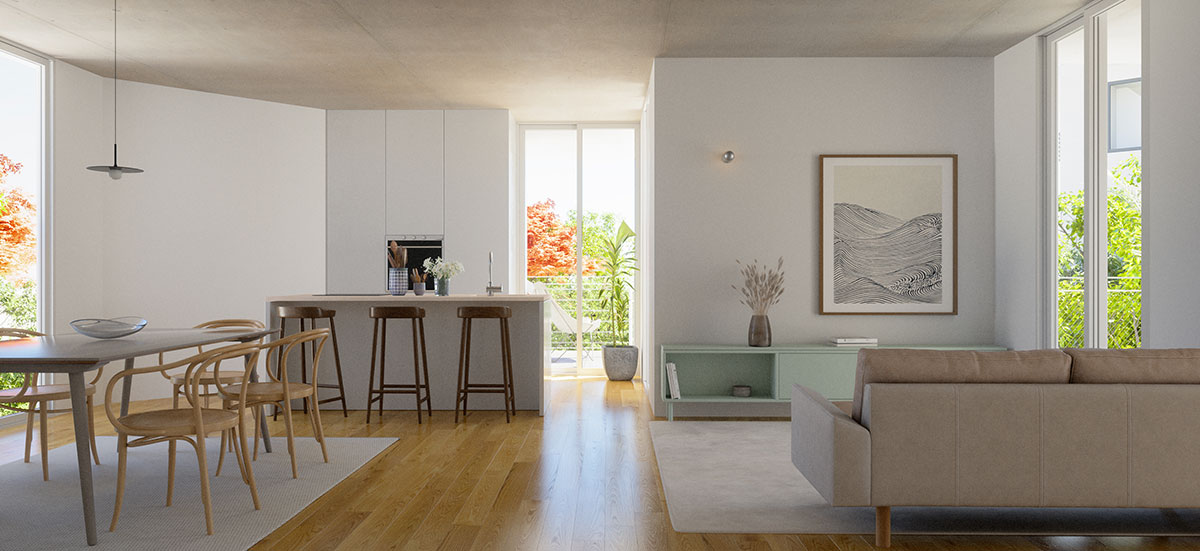

ENGINEERING PROJECT
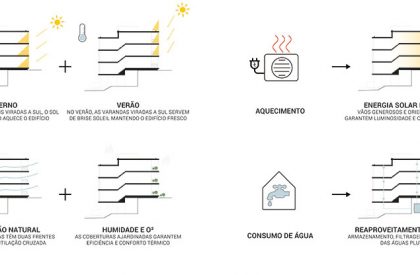
The building will be certified by the National System for Energy and Indoor Air Quality Certification of Buildings (SCE), intending to obtain an energy rating of good quality, so that all efforts will be made to optimize the operation of systems and minimize any energy losses, both at the project level and through careful implementation of the installation and assembly of its equipment.
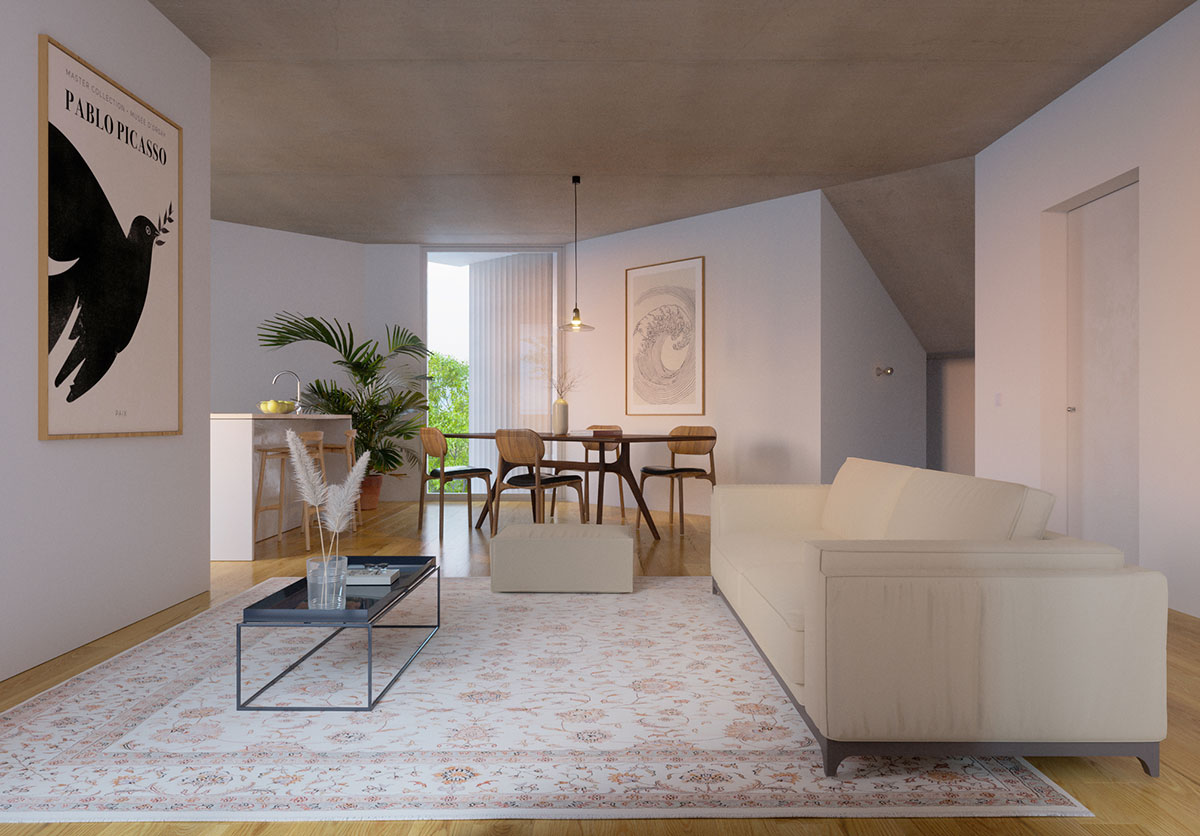

SOLAR PROTECTION/GLAZED AREAS
The proposed building will also be equipped with an external solar protection system, in the glazed areas, with an external shading screen, in order to reduce direct radiation into the building, thus avoiding an excessive increase of energy for cooling.
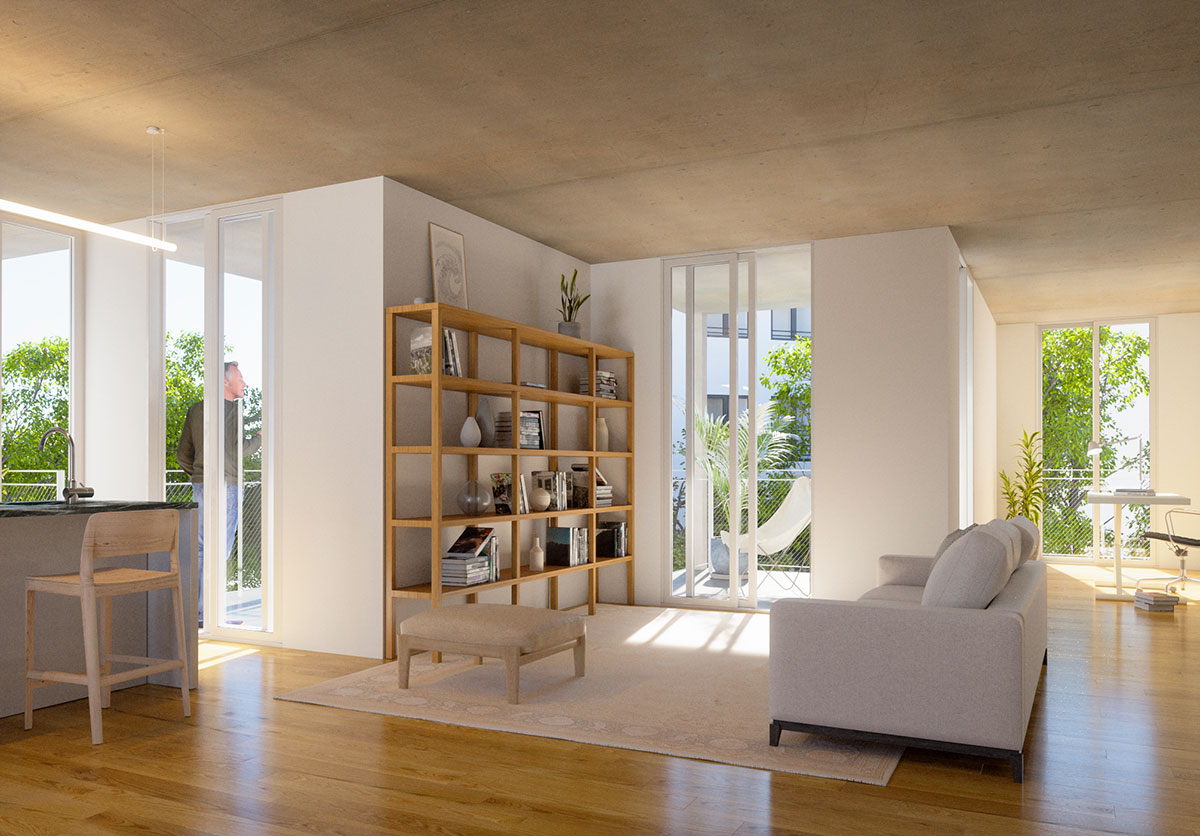

RENEWABLE ENERGY
For the heating of the hot water, solar thermal panels associated with monoblock-type heat pumps will be provided. One system of this type will be installed per building unit. As a complement to the renewable energy system, the installation of photovoltaic solar panels will also be proposed for the production of electricity to improve the energy rating and reduce electricity consumption.